
Fun facts about pH buffers
 The concept of pH buffers was originally born to meet the need for pH control in biochemical research. Growing mammalian cells in culture media is extremely pH-sensitive; adding a pH buffer can help to ensure that the pH does not fluctuate and inhibit growth.
The concept of pH buffers was originally born to meet the need for pH control in biochemical research. Growing mammalian cells in culture media is extremely pH-sensitive; adding a pH buffer can help to ensure that the pH does not fluctuate and inhibit growth.
 PH buffers that are nearly transparent have been produced to use in ultraviolet and invisible spectroscopy. The low pH range means that they are well-suited to spectrophotometric determinations.
PH buffers that are nearly transparent have been produced to use in ultraviolet and invisible spectroscopy. The low pH range means that they are well-suited to spectrophotometric determinations.
 PH buffers are used in the production of alcohol, being added before fermentation to ensure that the pH remains at a particular level to stop acidity, which would negatively impact the product. Because the fermentation process brings about pH changes, buffer solutions are a critical element of alcoholic drinks.
PH buffers are used in the production of alcohol, being added before fermentation to ensure that the pH remains at a particular level to stop acidity, which would negatively impact the product. Because the fermentation process brings about pH changes, buffer solutions are a critical element of alcoholic drinks.
 In many fabric dyeing processes, pH buffers are required to maintain the correct pH for the dye. Having an incorrect pH can alter the color of the dye while also reducing adherence to the fabric.
In many fabric dyeing processes, pH buffers are required to maintain the correct pH for the dye. Having an incorrect pH can alter the color of the dye while also reducing adherence to the fabric.
 PH buffers are used to manufacture many cosmetic and personal hygiene products to ensure that the pH remains neutral or marginally alkaline, reducing the risk of acidic or highly alkaline products causing skin irritation.
PH buffers are used to manufacture many cosmetic and personal hygiene products to ensure that the pH remains neutral or marginally alkaline, reducing the risk of acidic or highly alkaline products causing skin irritation.
What are pH Buffers?
PH buffers are special solutions which prevent large variations in pH levels. Every pH level produced has a specified buffer capacity and buffer range. The capacity of the buffer refers to the amount of acid or base which can be added before the pH alters substantially. It may also be characterized as the level of strong acid or base that needs to be added to alter the pH of a liter of solution by one pH unit. The buffer range is the pH range where a buffer can effectively neutralize added acids and bases while maintaining a steady pH. This is critical for processes or reactions which need specific and stable pH ranges. The pH of a solution is on a scale of 0-14 and is a temperature-dependent property.
Methods which utilize pH buffers
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Methods
- EPA 150.1 - Analysis of drinking, surface, saline, domestic and industrial wastes, and acid rain
- EPA 150.2 – Continuous pH measurement of the water sources listed in 150.1 above, except for acid rain
- EPA 150.3 – Analysis of drinking water
- SM4500-H+B – Electrometric method for water analysis (discusses concerns associated with mold and microbial growth)

The EPA and Standard Methods recommend a two-point calibration which brackets that of the pH range to be tested and indicates that these calibration points should be three or more pH units apart.
EPA 150.3 specifically recommends pH 7 and pH 10 for calibration points and pH 4 as a point to verify the calibration. Secondary buffers should be used that have been validated against NIST standards.
United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and European Pharmacopeia (EP) Methods
- USP <791> – Potentiometric determination of pH of pharmaceutical and patient care products, food and beverage, and supplements
- EP 2.2.3 – Potentiometric determination of pH in quality control of pharmaceutical products
The USP and EP standards for testing pharmaceutical products outline very similar methods by which these analyses should be conducted. In both methods, a calibration curve of at least two points is necessary.
However, the EP outlines a calibration procedure in which pH 4 is always used in conjunction with another buffer of a different pH (often seen as pH 4 and pH 10).
The USP method dictates that the meter must be calibrated with at least two buffers, with a difference between them of no more than 4, and the expected pH of the sample being analyzed must fall between the buffers selected (often pH 4, pH 7, and pH 10 are used).
Temperature requirements also differ between these methods; EP 2.2.3 dictates that measurements must be made at the same temperature, which must fall between 20-25?C, while USP <791> indicates a temperature range of 25 ± 2?C.
Finally, and possibly most importantly, the margin of error allowed by the two methods differ notably. EPA 2.2.3 states that the value of the buffer used to verify calibration cannot differ by more than 0.05pH; USP <791> describes a smaller range – calibration standards may not differ from results obtained by more than ±0.02pH.
Both the USP and EP are legally binding and enforceable by respective government agencies, as they each play an important role in maintaining the health and safety of the localities for which they were written.
pH buffers from Inorganic Ventures
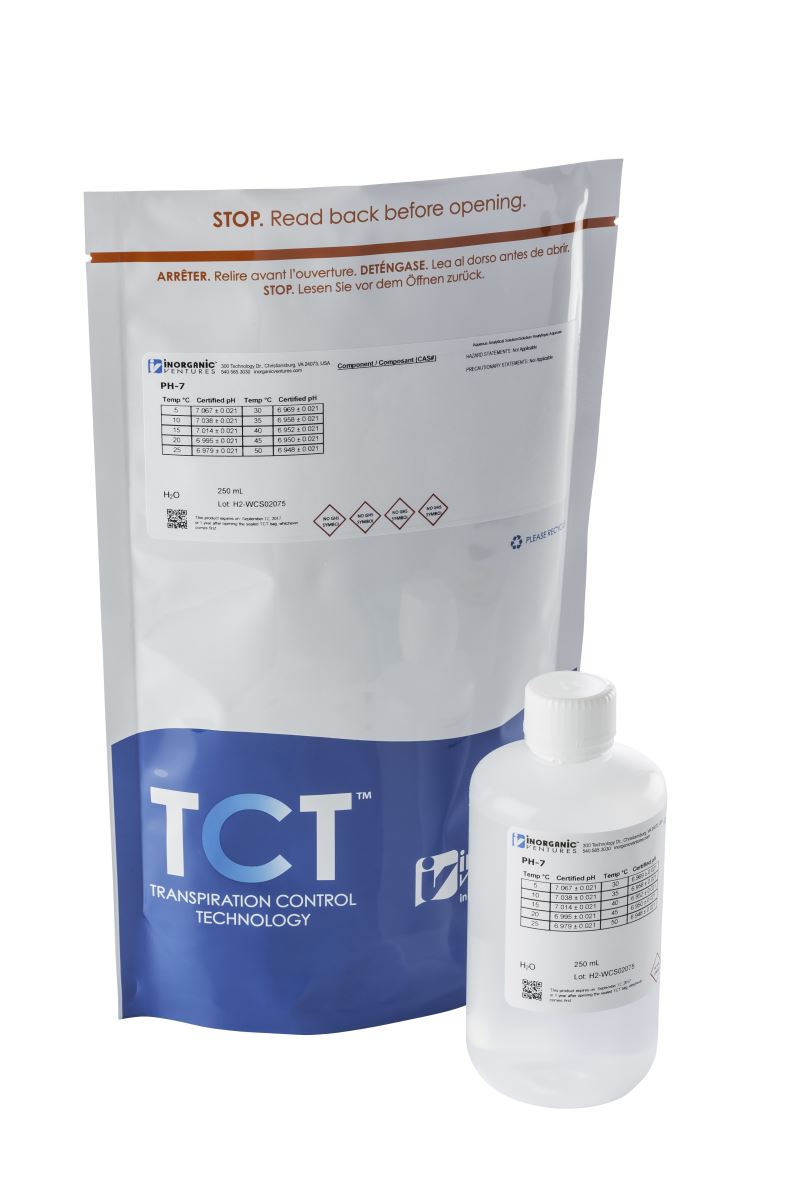
For analysts tasked with maintaining proper pH meter calibration in accordance with the methods listed above, Inorganic Ventures’ CRMs deliver confidence, control and support.
Our pH buffers are NIST-traceable and manufactured and tested under ISO 17034 and ISO 17025 guidelines. Each standard is accompanied by a detailed Certificate of Analysis (CoA), displaying certified values for multiple temperatures.
- NIST-traceable standards, certified within 5% of the nominal values and associated uncertainties of no more than 0.05 pH units
- Packaged in Transpiration Control Technology (TCT) which guarantees scientific integrity for up to 5-years from the date of manufacture.
- Proprietary microbial prevention agent ensures that the buffers arrive to your lab ready to use and safe to count on for all your pH analysis needs.
Product Offerings:
pH 4, pH 7 and pH 10 are available in colored solutions here.